

There are bright regions of the sound away from the direct path out of the window. This is because the wavelength of the sound waves in air is comparable to the size of the window.

In acoustics, this is called the "Far field approximation". of the light (barring some strong reflection), you will likely hear the sound. But for point further away it works quite well. Keep in mind that this only applies for being "far away" from the source of the sound, because the power/area would be infinite at your mouth, since you would be dividing through a surface area of 0. Typical to all current coaxial designs is somewhat ragged frequency response. The diffraction of water waveswas discussed in Unit 10 of The Physics Classroom Tutorial. Minimum Diffraction Coaxial (MDC) transducer reproduces outstanding sound image. Now everything has 16 times the power / area in that direction and suddenly you're much louder at 2m distance than you were before in even 1m distance. Diffraction involves a change in direction of waves as they pass through an opening or around a barrier in their path. For example, in the picture below, the sound waves from the explosion. Instead of evenly distributing the sound over the shell, you're focussing it on let's say on 1/16 of the surface. When a wave is diffracted it spreads out around the object it hit. Refraction is when waves, whether physical or electromagnetic, are deflected when. A mirror reflects the image of the observer. Reflection is when waves, whether physical or electromagnetic, bounce from a surface back toward the source. That's why your voice gets quiter with distance. The wall may stop, but the voice doesnt sound will almost turn the corner of the wall. The importance of diffraction in any given situation depends on the relative size of the obstacle or opening and the wavelength of the wave striking it. So there is only 1/4 the power per surface area than in 1m distance from your mouth. Diffraction is the deviation of a traveling wave (light, sound, or other) from a straight path that occurs when the wave passes around an obstacle or through an opening. At 2m distance, that shell has a radius of 2m and four times the surface area. In 1m distance, that shell has a radius of 1m.
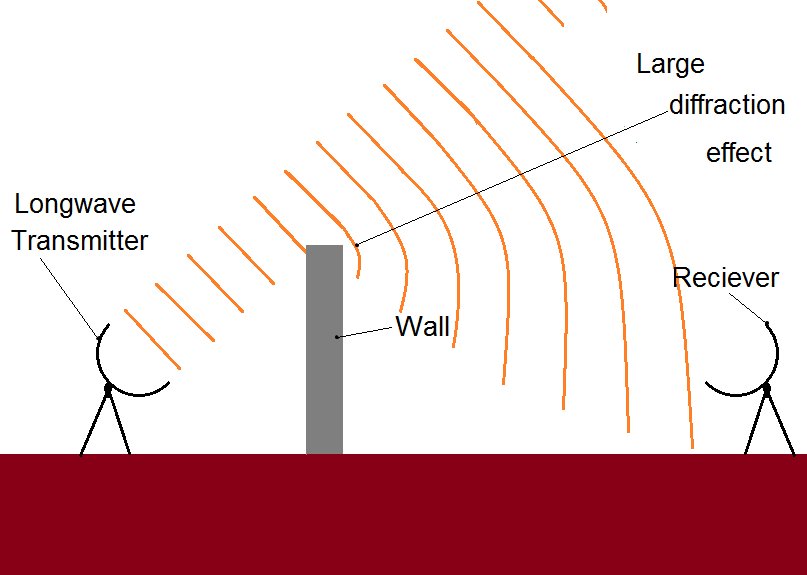
Various geological features and coastal oceanographic processes can cause horizontal reflection, refraction, and diffraction of underwater sound. Diffraction: the bending of waves around small obstacles and the spreading out of waves beyond small openings. If these waves would evenly distribute around you, imagine all that Energy distributing on a "shell" around you. Three-dimensional (3D) effects can profoundly influence underwater sound propagation in shallow-water environments, hence, affecting the underwater soundscape. Let's say your mouth emits sound waves that carry a power P. It basically boils down to conservation of energy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
